guide_geo behaves similarly to ggplot2::guide_axis() in that it modifies
the visual appearance of the axis. The main difference is that it adds a
geological timescale instead of an axis.
Usage
guide_geo(
dat = "periods",
fill = NULL,
alpha = 1,
height = unit(2, "line"),
bord = c("left", "right", "top", "bottom"),
lwd = 0.25,
color = "black",
lab = TRUE,
lab_color = NULL,
rot = 0,
family = "sans",
fontface = "plain",
size = 5,
skip = c("Quaternary", "Holocene", "Late Pleistocene"),
abbrv = TRUE,
neg = FALSE,
end_labels = "center",
dat_is_discrete = FALSE,
fittext_args = list(),
theme = NULL,
title = waiver(),
order = 0,
position = waiver()
)Arguments
- dat
Either A) a string indicating a built-in dataframe with interval data from the ICS ("periods", "epochs", "stages", "eons", or "eras"), B) a string indicating a timescale from macrostrat (see list here: https://macrostrat.org/api/defs/timescales?all), or C) a custom data.frame of time interval boundaries (see Details).
- fill
The fill color of the boxes. The default is to use the
colorcolumn included indat. If a custom dataset is provided withdatwithout acolorcolumn and without fill, a greyscale will be used. Custom fill colors can be provided with this option (overriding thecolorcolumn) and will be recycled if/as necessary.- alpha
The transparency of the fill colors.
- height
The height (or width if
posisleftorright) of the scale.- bord
A vector specifying on which sides of the scale to add borders (same options as
pos).- lwd
Line width.
- color
The outline color of the interval boxes.
- lab
Whether to include labels.
- lab_color
The color of the labels. The default is to use the
lab_colorcolumn included indat. If a custom dataset is provided withdatwithout alab_colorcolumn and without fill, all labels will be black. Custom label colors can be provided with this option (overriding thelab_colorcolumn) and will be recycled if/as necessary.- rot
The amount of counter-clockwise rotation to add to the labels (in degrees).
- family
The font family to use for the labels. There are only three fonts that are guaranteed to work everywhere: “sans” (the default), “serif”, or “mono”.
- fontface
The font face to use for the labels. The standard options are "plain" (default), "bold", "italic", and "bold.italic".
- size
Label size. Either a number as you would specify in
ggplot2::geom_text()or"auto"to useggfittext::geom_fit_text().- skip
A vector of interval names indicating which intervals should not be labeled. If
abbrvisTRUE, this can also include interval abbreviations.- abbrv
If including labels, should the labels be abbreviated? If
TRUE, theabbrcolumn will be used for the labels. IfFALSE, thenamecolumn will be used for the labels. If"auto", theabbreviate()function will be used to abbreviate the values in thenamecolumn. Note that the built-in data and data retrieved viaget_scale_data()already have built-in abbreviations. However, using the"auto"option here will create new unique abbreviations based on only the intervals that are being plotted. In many cases, this may result in abbreviations that are shorter in length because there are fewer similar interval names to abbreviate.- neg
Set this to
TRUEif your x-axis is using negative values.- end_labels
How should labels for intervals at the ends of the guide be treated? "center", the default, centers the labels within the visible part of the label. "clip" removes the labels if their midpoint is beyond the axis limits. "keep" plots the labels in the midpoint of the full interval.
- dat_is_discrete
Are the ages in
datalready converted for a discrete scale?- fittext_args
A list of named arguments to provide to
ggfittext::geom_fit_text(). Only used ifsizeis set to"auto".- theme
A
themeobject to style the guide individually or differently from the plot's theme settings. Thethemeargument in the guide partially overrides, and is combined with, the plot's theme.- title
A character string or expression indicating a title of guide. If
NULL, the title is not shown. By default (waiver()), the name of the scale object or the name specified inlabs()is used for the title.- order
A positive
integerof length 1 that specifies the order of this guide among multiple guides. This controls in which order guides are merged if there are multiple guides for the same position. If 0 (default), the order is determined by a secret algorithm.- position
Where this guide should be drawn: one of top, bottom, left, or right.
Details
If a custom data.frame is provided (with dat), it should consist of at
least 3 columns of data. See data(periods) for an example.
The
namecolumn lists the names of each time interval. These will be used as labels if no abbreviations are provided.The
max_agecolumn lists the oldest boundary of each time interval.The
min_agecolumn lists the youngest boundary of each time interval.The
abbrcolumn is optional and lists abbreviations that may be used as labels.The
colorcolumn is also optional and lists a color for the background for each time interval.The
lab_colorcolumn is also optional and lists a color for the label for each time interval.
If the axis of the time scale is discrete, max_age and min_age will
automatically be converted to the discrete scale. In this case, the
categories of the discrete axis should match the values in the name column.
If the ages within dat are already discretized, you can set
dat_is_discrete to TRUE to prevent this automatic conversion. This can be
useful for adding a time scale where categories and time intervals are not
1:1.
Since this guide only plots the timescale and not ticks or an axis line, a
call to this function should almost always be combined with a call to
ggplot2::guide_axis() within a call to ggplot2::guide_axis_stack() (see
Examples). Note that in most cases this has the same end result as a single
call to coord_geo(); however, there are some use cases in which this may be
more useful or allow for more customization. For example, users may wish to
combine this guide in unique ways with other guides. Further, since
coord_geo() doesn't work with radial/fan phylogenies (and
coord_geo_radial() is quite different visually), this guide can be used to
achieve the look of coord_geo() on a radial/fan phylogeny.
Examples
library(ggplot2)
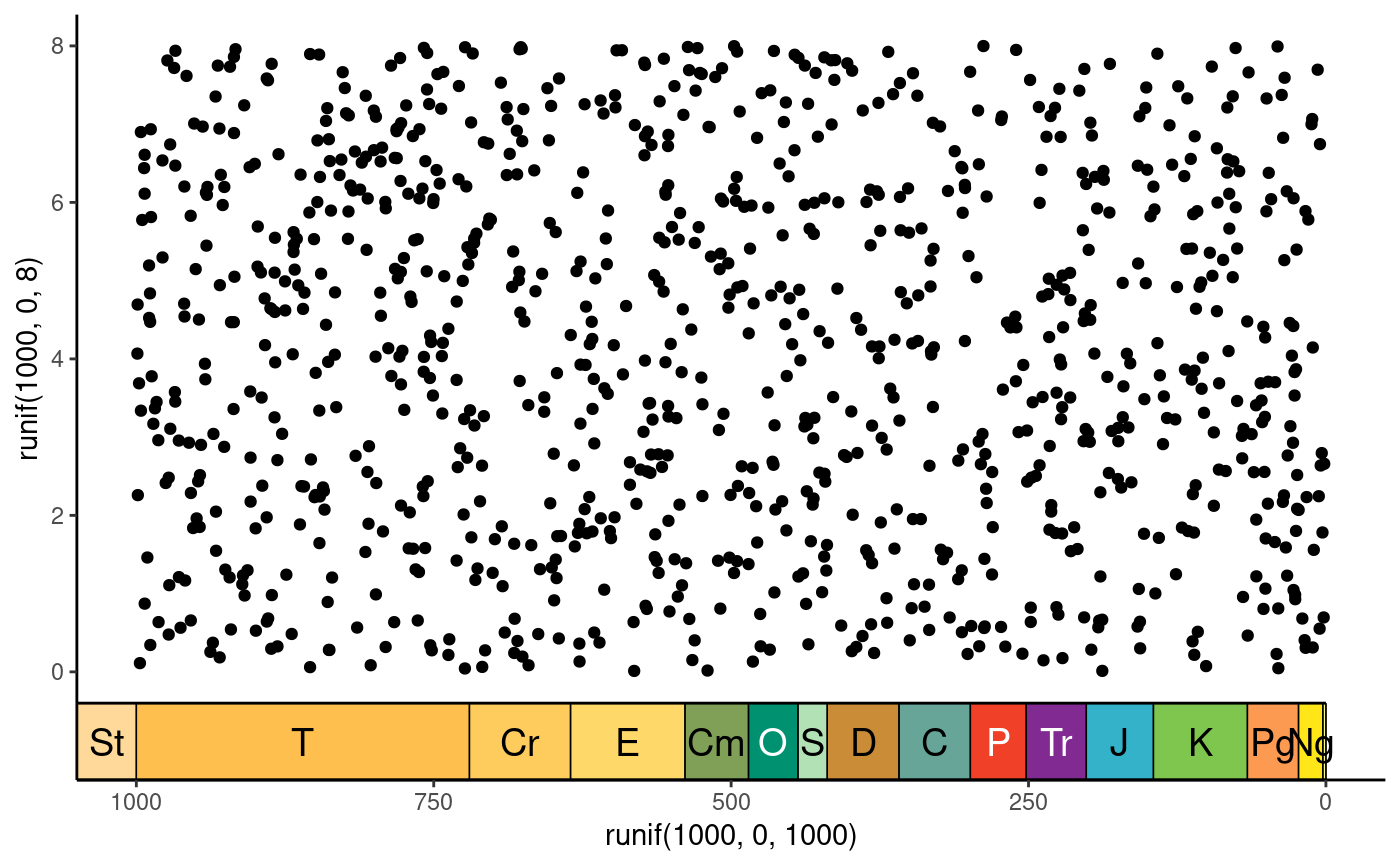
# reproduce the coord_geo() appearance
ggplot() +
geom_point(aes(y = runif(1000, 0, 8), x = runif(1000, 0, 1000))) +
scale_x_reverse(guide = guide_axis_stack(guide_geo(), "axis",
spacing = unit(0, "npc"))) +
coord_cartesian(xlim = c(1000, 0), ylim = c(0, 8)) +
theme_classic()
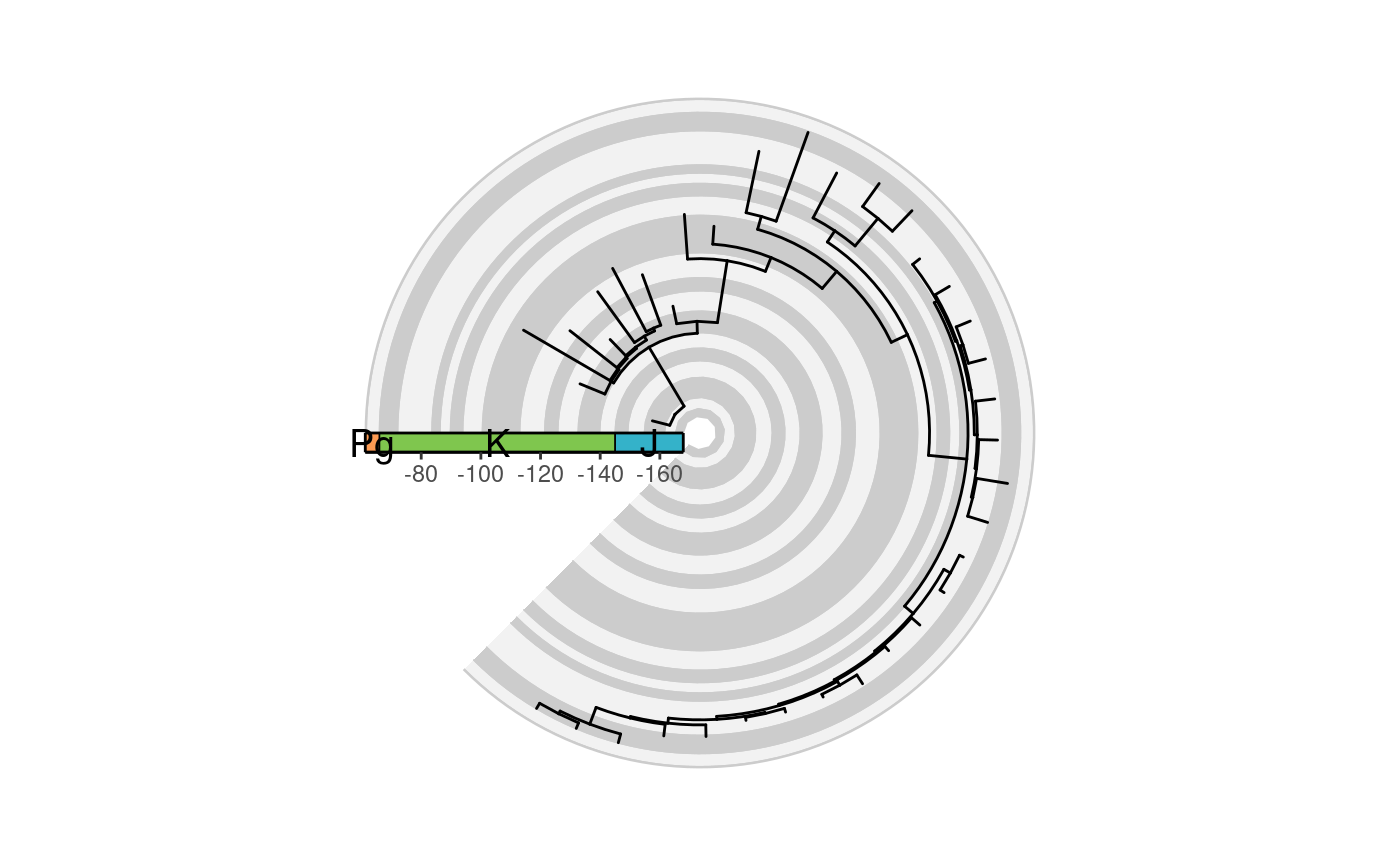
 # the coord_geo() look on a radial phylogeny
library(ggtree)
library(paleotree)
data(RaiaCopesRule)
ggtree(ceratopsianTreeRaia,
position = position_nudge(x = -ceratopsianTreeRaia$root.time)) +
coord_geo_radial(dat = "stages", fill = c("grey80", "grey95"),
end = 1.25 * pi) +
guides(
r = guide_axis_stack(guide_geo(rot = -90, neg = TRUE,
height = unit(0.5, "line")),
"axis", spacing = unit(0, "npc"))
) +
scale_y_continuous(guide = "none", breaks = NULL) +
theme_classic()
#> Scale for y is already present.
#> Adding another scale for y, which will replace the existing scale.
#> Warning: Unknown or uninitialised column: `subgroup`.
#> Warning: Unknown or uninitialised column: `subgroup`.
#> Warning: Unknown or uninitialised column: `subgroup`.
#> Warning: Unknown or uninitialised column: `subgroup`.
# the coord_geo() look on a radial phylogeny
library(ggtree)
library(paleotree)
data(RaiaCopesRule)
ggtree(ceratopsianTreeRaia,
position = position_nudge(x = -ceratopsianTreeRaia$root.time)) +
coord_geo_radial(dat = "stages", fill = c("grey80", "grey95"),
end = 1.25 * pi) +
guides(
r = guide_axis_stack(guide_geo(rot = -90, neg = TRUE,
height = unit(0.5, "line")),
"axis", spacing = unit(0, "npc"))
) +
scale_y_continuous(guide = "none", breaks = NULL) +
theme_classic()
#> Scale for y is already present.
#> Adding another scale for y, which will replace the existing scale.
#> Warning: Unknown or uninitialised column: `subgroup`.
#> Warning: Unknown or uninitialised column: `subgroup`.
#> Warning: Unknown or uninitialised column: `subgroup`.
#> Warning: Unknown or uninitialised column: `subgroup`.